Bioremediation
More Info
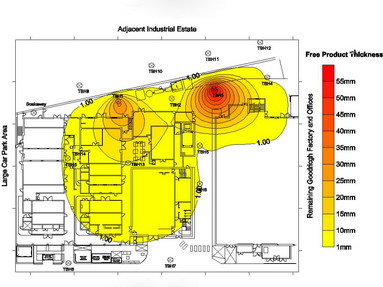
TRM offers a large range of in situ and ex situ remediation techniques in the UK. A combination of experience and expertise, our technologies comprise:
Often more than one type of remediation technology will be required for a site with multiple contamination issues and in such instances, TRM will provide a range of combined technologies designed specifically to suit each project.
The remediation of land and groundwater has waste permitting implications and is subject to waste management licensing. Our technologies are undertaken by our mobile plant permit GP3895FL.
Take a closer look at some of our remediation technologies.